Abstract
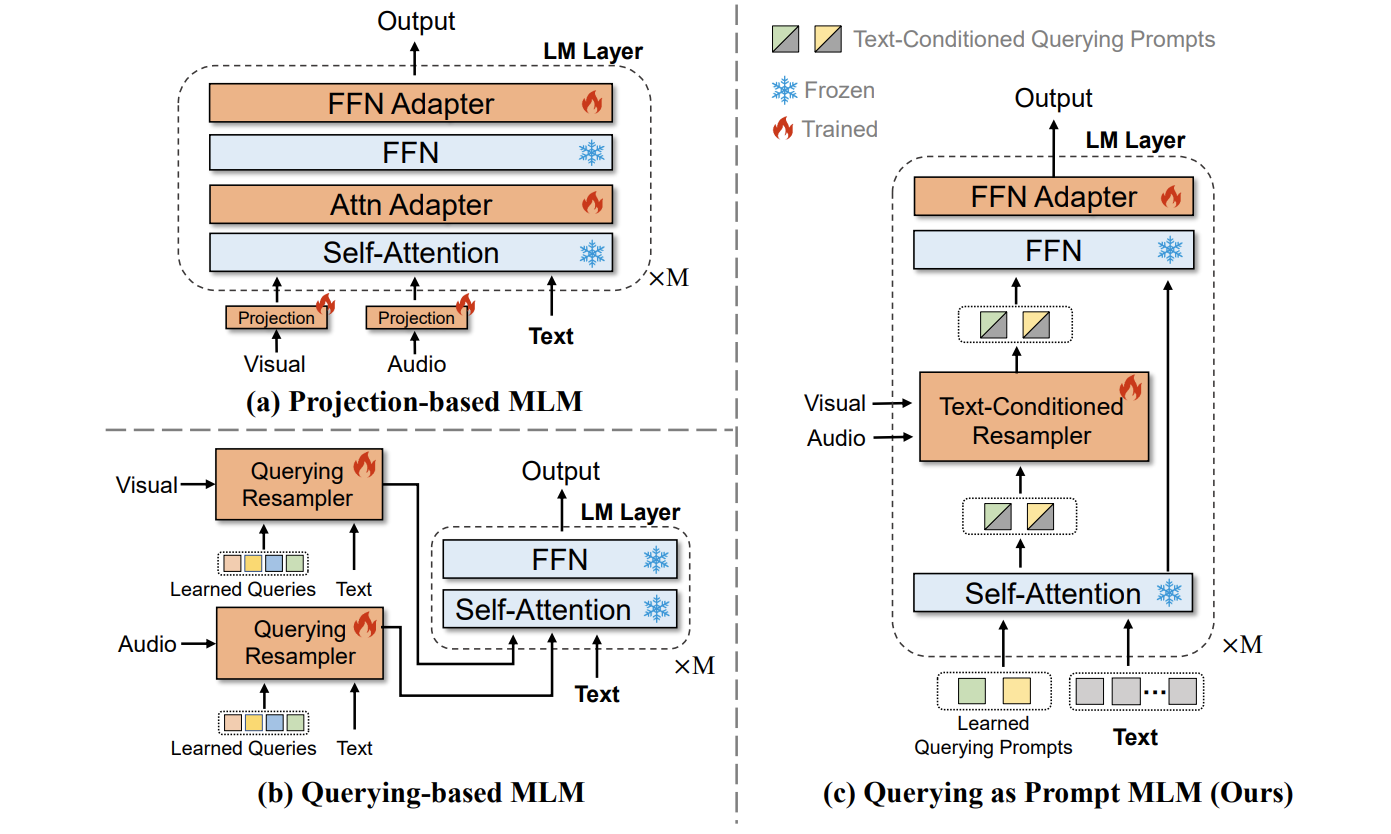
Recent advancements in language models pre-trained on large-scale corpora have signifcantly propelled developments in the NLP domain and advanced progress in multimodal tasks. In this paper, we propose a Parameter Effcient multimodal language model learning strategy, named QaP $($Querying as Prompt$)$. Its core innovation is a novel modality-bridging method that allows a set of modality-specifc queries to be input as soft prompts into a frozen pre-trained language model. Specifcally, we introduce an effcient Text-Conditioned Resampler that is easy to incorporate into the language models, which enables adaptive injection of text-related multimodal information at different levels of the model through query learning. This approach effectively bridges multimodal information to the language models while fully leveraging its token fusion and representation potential. We validated our method across four datasets in three distinct multimodal tasks. The results demonstrate that our QaP multimodal language model achieves state-of-the-art performance in various tasks with training only 4.6% parameters.
- Task: Multimodal Language Model
- Problem Definition: $($Not defined in the abstract$)$ Computation cost, parameter inefficiency
- Approach: Allowing a set of modality-specific queries to be input as soft prompts into a frozen pre-trained language model
*Soft Prompts: soft prompts are learnable tensors concatenated with the input embeddings that can be optimized to a dataset; the downside is that they aren’t human readable because you aren’t matching these “virtual tokens” to the embeddings of a real word